What is the difference between X-ray, CT, B- ultrasound and magnetic resonance?
2016-05-14
X-ray photography (plain film)
X-rays will pass through the human body and absorb rays in different parts. The negative will not be exposed or partially exposed. This part will be white after film washing.
Advantages: fast and cheap.
Disadvantages: Subject to the deep tissue of the image overlap and hidden, sometimes need to take multiple multi-angle X-ray to see.
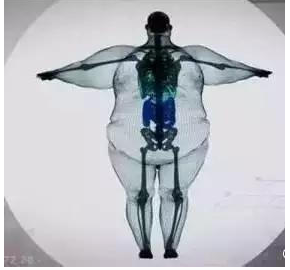
(900kg man under X-ray)
C T
The inspection principle of CT is that X-ray will slice through the human body and post-process it into secondary imaging through computer calculation.
Advantages: It can be seen from the fault, and more information can be displayed after post-processing.
Disadvantages: The cost is more expensive than X-ray photography, and the radiation dose of CT examination is usually higher than that of single X-ray photography.
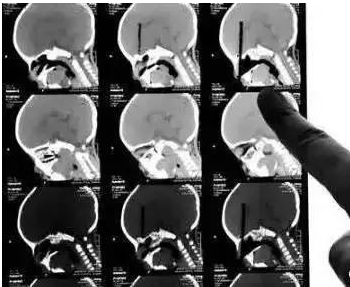
CT 3D reconstruction of chopsticks inserted into the eyeball)
B ultrasound
The principle of B ultrasound is to use ultrasonic waves to penetrate the human body. When the sound waves encounter human tissue, they will produce reflected waves, which are imaged by calculating the reflected waves.
Advantages: Multi-directional observation, real-time imaging.
Disadvantages: Ultrasound is greatly interfered by gas. For organs with more gas such as intestinal tract, the accuracy rate of ultrasound diagnosis will be reduced, so colonoscopy is generally used for intestinal examination.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Magnetic resonance imaging is an imaging technology that uses the signals generated by collecting magnetic resonance phenomena to reconstruct images. Simply put, it is equivalent to shaking the hydrogen protons by hand to vibrate, then calm down and feel the vibration inside.
Advantages: Compared with CT, it has no radiation, no bone artifacts, can be multi-faceted, multi-parameter imaging, and has a high degree of soft tissue resolution.
Disadvantages: relatively expensive.
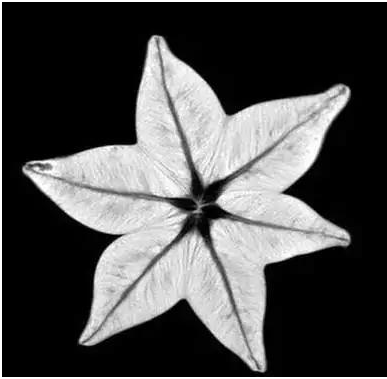
(star fruit under the nuclear magnetic resonance)
Which body parts are suitable for which examination
1. Traumatic Bones-Take a rough look at X-ray photography and CT carefully. When encountering various traumas, if bones are suspected to be injured, X-ray photography is preferred, and the examination results are quick and easy to obtain. For further observation, CT observation details or even MRI observation of occult or soft tissue damage may be selected.
2, cervical and lumbar spine-the best choice of magnetic resonance imaging, the second choice of CT cervical spondylosis, lumbar disc herniation and other intervertebral disc diseases need to observe the intervertebral disc and the corresponding nerve root, in order to better observe these soft tissues, the best choice is magnetic resonance imaging. Similarly, magnetic resonance imaging is also a good choice for the examination of joints, muscles, adipose tissue, tumors, inflammation, trauma, degenerative diseases and various congenital diseases. CT can be used as a powerful supplement to observe spinal bone hyperplasia and intervertebral foramen stenosis.
3. Chest-roughly look at X-ray plain film, carefully look at CTX-ray chest film can roughly check lung, heart shadow, aortic arch, ribs, etc., and can check whether there is increased lung texture, large mass in lung, aortic node calcification, etc. Chest CT examination shows a clearer structure, and the sensitivity and accuracy of chest lesions detection are better than regular chest X-ray, especially for the screening of early lung cancer is of great significance. The application of magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of pulmonary diseases is very limited.
4. Abdominal and pelvic cavities-in addition to intestinal tract, the general ultrasound can check the well-known examination of the fetus during pregnancy, which can be seen clearly with B- ultrasound. In addition, superficial organs such as thyroid gland, as well as parenchymal organs such as liver, spleen, pancreas, kidney and pelvic cavity, have high diagnostic accuracy of B- ultrasound.
5. Heart-CT is used to exclude coronary heart disease, and cardiac structure and function examination regular by ultrasound are used to see cardiac function. Cardiac color Doppler ultrasound can almost satisfy! If the examination of coronary arteries, structural abnormalities of congenital heart disease can be used CT. Magnetic resonance imaging is used to examine myocardial lesions, such as myocardial infarction.
E-mail:jsgc@jsguanchuang.com
Mobile:19851910098
Contact address: 3C, Wujin Science and Technology Innovation Park, No. 256 Mingxin Middle Road, Wujin District, Changzhou City, Jiangsu Province
Quick Links
Message
We will contact you within one working day. Please pay attention to your email.
